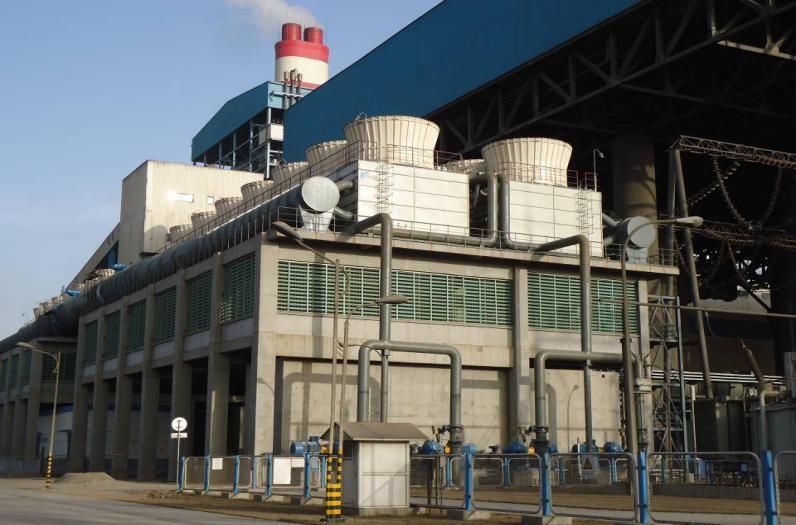
Longhua specializes in evaporative cooled condensers and offers tailored solutions for our clients. Our evaporative condensers utilize advanced Evaporative Cooled Condenser Technology, renowned for its high heat transfer performance, water efficiency, and energy savings.
Replace sensible heat exchange with latent heat exchange (advanced heat exchange mechanism, energy-saving and water-saving)
Heating 1 kg of water by 1℃ removes 1 kcal of heat, while evaporating 1 kg of water removes 580 kcal of heat. With an 8℃ temperature rise, the ratio remains 70 times. It requires a small amount of circulating water, saving energy, and consumes a small amount of water, saving water.
Strong combination of heat release during condensation and heat absorption during evaporation (highest efficiency)
Heat release occurs inside the tube during condensation, while heat absorption occurs outside the tube during evaporation, both undergoing phase change, resulting in the highest efficiency.
The lower limit temperature for cooling is the wet-bulb temperature (strong heat exchange driving force or low cooling temperature)
The wet-bulb temperature is generally 8-14℃ lower than the dry-bulb temperature, even lower than the condensing temperature compared to water cooling.
The system is simple and all heat exchange occurs in one stage (direct heat exchange)
Both belong to direct condensation with direct air cooling, either in parallel or in series, keeping the system simple and consistent.
Evaporative condensers operate on the principle of evaporative cooling, where water is used as the cooling medium to remove heat from process fluids. The cooled water is then recycled and reused, making it an energy-efficient cooling solution.
The operational principles of evaporative-cooled condensers are as follows:
1. The exhaust steam of the low-pressure cylinder of the steam turbine enters the tube of the heat exchange module by condensing and releasing heat;
2. The spray water outside the pipe absorbs the condensation and exothermic evaporation of the steam in the pipe, which is discharged into the atmosphere under the action of the fan, and the water lost by evaporation is supplemented by the water supply pipeline; The unevaporated water is recycled into the water tank by the action of the water collector.
3. Condensate water is collected in the exhaust steam unit hot well through the pipeline.
4. Non-condensable gas is discharged by the vacuum device.
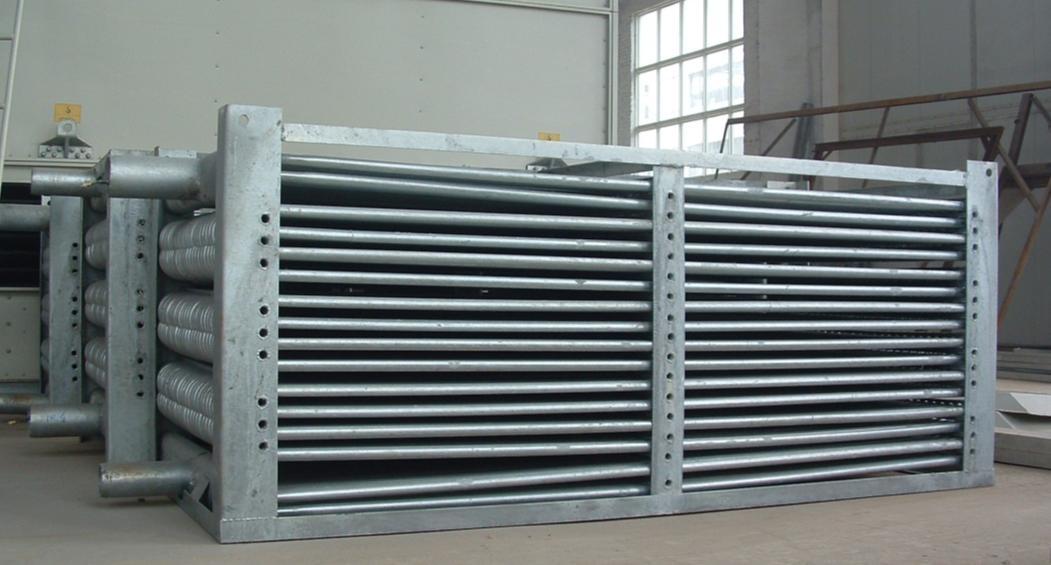
An evaporative condenser is typically made up of a tube bundle that is arranged in horizontal coils through which a warm fluid circulates. Water is sprayed over the tubes and evaporates, removing heat from the process fluid. The latent heat required to evaporate the water comes from the heat rejected by the process fluid being condensed. As the water evaporates, it becomes saturated with heat and is collected at the bottom of the condenser. It is then pumped to the top of the condenser, where it is sprayed again to continue the heat transfer process.
Evaporative type condensers can be used in both closed and open-loop systems, depending on the application. They are used in various industries to cool process fluids in refrigeration, air conditioning, and power generation applications. They offer several advantages, including high efficiency and energy savings, and are suitable for use in areas with limited space.
Evaporative type condensers require anti-corrosion measures due to the presence of water in the system. Water can lead to corrosion of metal components over time, especially in environments with high humidity or when the water used in the system contains impurities or chemicals. Anti-corrosion measures are implemented to protect the evap condenser's structural integrity, ensuring its longevity and optimal performance.
Longhua, a dedicated manufacturer of evaporative cooled condensers, prioritizes anti-corrosion measures for Evaporative Type Condensers. During the production process, we conduct overall hot-dip galvanizing anti-corrosion treatment on the heat exchange module. Our anti-corrosion treatment procedures are outlined below:
Degreasing with acidic degreasing agent (oil removal) → Rust removal with composite rust remover → Warm water rinsing → Clear water rinsing → Assist plating (assist plating agent removes iron) → Drying → Hot-dip galvanizing (thickness 80-120μm, metal bonding layer 5μm) → Water cooling → Passivation → Inspection → Forming



 EN
EN